Expo
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
RadiographyMRIUltrasoundNuclear Medicine
Imaging ITIndustry News
Events

- AI Assistance Improves Breast-Cancer Screening by Reducing False Positives
- AI Could Boost Clinical Adoption of Chest DDR
- 3D Mammography Almost Halves Breast Cancer Incidence between Two Screening Tests
- AI Model Predicts 5-Year Breast Cancer Risk from Mammograms
- Deep Learning Framework Detects Fractures in X-Ray Images With 99% Accuracy
- Diamond Dust Could Offer New Contrast Agent Option for Future MRI Scans
- Combining MRI with PSA Testing Improves Clinical Outcomes for Prostate Cancer Patients
- PET/MRI Improves Diagnostic Accuracy for Prostate Cancer Patients
- Next Generation MR-Guided Focused Ultrasound Ushers In Future of Incisionless Neurosurgery
- Two-Part MRI Scan Detects Prostate Cancer More Quickly without Compromising Diagnostic Quality
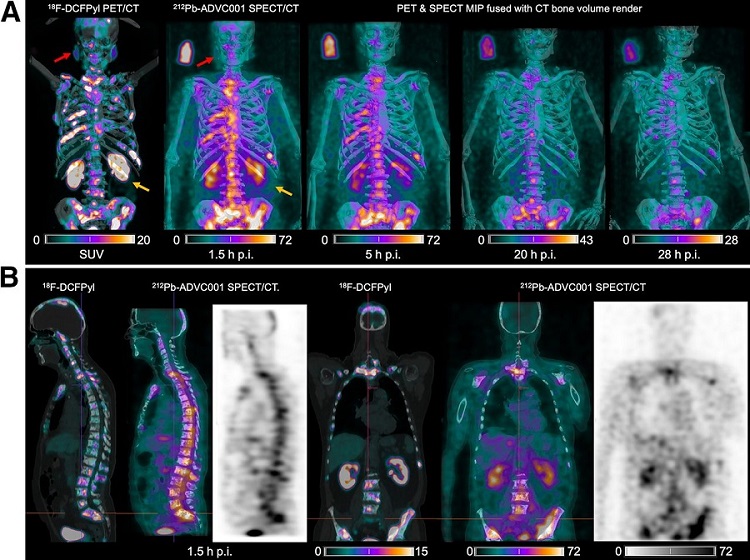
- New SPECT/CT Technique Could Change Imaging Practices and Increase Patient Access
- New Radiotheranostic System Detects and Treats Ovarian Cancer Noninvasively
- AI System Automatically and Reliably Detects Cardiac Amyloidosis Using Scintigraphy Imaging
- Early 30-Minute Dynamic FDG-PET Acquisition Could Halve Lung Scan Times
- New Method for Triggering and Imaging Seizures to Help Guide Epilepsy Surgery
- Groundbreaking Technology Enables Precise, Automatic Measurement of Peripheral Blood Vessels
- Deep Learning Advances Super-Resolution Ultrasound Imaging
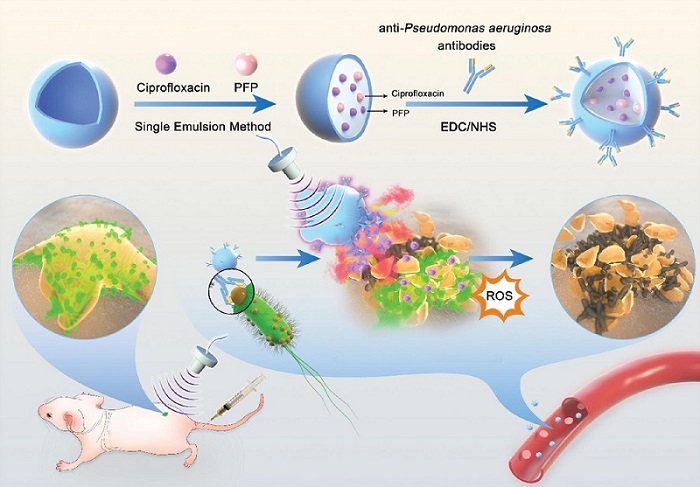
- Novel Ultrasound-Launched Targeted Nanoparticle Eliminates Biofilm and Bacterial Infection
- AI-Guided Ultrasound System Enables Rapid Assessments of DVT
- Focused Ultrasound Technique Gets Quality Assurance Protocol
- Artificial Intelligence Evaluates Cardiovascular Risk from CT Scans
- New AI Method Captures Uncertainty in Medical Images
- CT Coronary Angiography Reduces Need for Invasive Tests to Diagnose Coronary Artery Disease
- Novel Blood Test Could Reduce Need for PET Imaging of Patients with Alzheimer’s
- CT-Based Deep Learning Algorithm Accurately Differentiates Benign From Malignant Vertebral Fractures
- Global AI in Medical Diagnostics Market to Be Driven by Demand for Image Recognition in Radiology
- AI-Based Mammography Triage Software Helps Dramatically Improve Interpretation Process
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) Program Accurately Predicts Lung Cancer Risk from CT Images
- Image Management Platform Streamlines Treatment Plans
- AI Technology for Detecting Breast Cancer Receives CE Mark Approval
- Samsung and Bracco Enter Into New Diagnostic Ultrasound Technology Agreement
- IBA Acquires Radcal to Expand Medical Imaging Quality Assurance Offering
- International Societies Suggest Key Considerations for AI Radiology Tools
- Samsung's X-Ray Devices to Be Powered by Lunit AI Solutions for Advanced Chest Screening
- Canon Medical and Olympus Collaborate on Endoscopic Ultrasound Systems

Expo
 view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
RadiographyMRIUltrasoundNuclear Medicine
Imaging ITIndustry News
Events
Advertise with Us
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
RadiographyMRIUltrasoundNuclear Medicine
Imaging ITIndustry News
Events
Advertise with Us


- AI Assistance Improves Breast-Cancer Screening by Reducing False Positives
- AI Could Boost Clinical Adoption of Chest DDR
- 3D Mammography Almost Halves Breast Cancer Incidence between Two Screening Tests
- AI Model Predicts 5-Year Breast Cancer Risk from Mammograms
- Deep Learning Framework Detects Fractures in X-Ray Images With 99% Accuracy
- Diamond Dust Could Offer New Contrast Agent Option for Future MRI Scans
- Combining MRI with PSA Testing Improves Clinical Outcomes for Prostate Cancer Patients
- PET/MRI Improves Diagnostic Accuracy for Prostate Cancer Patients
- Next Generation MR-Guided Focused Ultrasound Ushers In Future of Incisionless Neurosurgery
- Two-Part MRI Scan Detects Prostate Cancer More Quickly without Compromising Diagnostic Quality
- New SPECT/CT Technique Could Change Imaging Practices and Increase Patient Access
- New Radiotheranostic System Detects and Treats Ovarian Cancer Noninvasively
- AI System Automatically and Reliably Detects Cardiac Amyloidosis Using Scintigraphy Imaging
- Early 30-Minute Dynamic FDG-PET Acquisition Could Halve Lung Scan Times
- New Method for Triggering and Imaging Seizures to Help Guide Epilepsy Surgery
- Groundbreaking Technology Enables Precise, Automatic Measurement of Peripheral Blood Vessels
- Deep Learning Advances Super-Resolution Ultrasound Imaging
- Novel Ultrasound-Launched Targeted Nanoparticle Eliminates Biofilm and Bacterial Infection
- AI-Guided Ultrasound System Enables Rapid Assessments of DVT
- Focused Ultrasound Technique Gets Quality Assurance Protocol
- Artificial Intelligence Evaluates Cardiovascular Risk from CT Scans
- New AI Method Captures Uncertainty in Medical Images
- CT Coronary Angiography Reduces Need for Invasive Tests to Diagnose Coronary Artery Disease
- Novel Blood Test Could Reduce Need for PET Imaging of Patients with Alzheimer’s
- CT-Based Deep Learning Algorithm Accurately Differentiates Benign From Malignant Vertebral Fractures
- Global AI in Medical Diagnostics Market to Be Driven by Demand for Image Recognition in Radiology
- AI-Based Mammography Triage Software Helps Dramatically Improve Interpretation Process
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) Program Accurately Predicts Lung Cancer Risk from CT Images
- Image Management Platform Streamlines Treatment Plans
- AI Technology for Detecting Breast Cancer Receives CE Mark Approval
- Samsung and Bracco Enter Into New Diagnostic Ultrasound Technology Agreement
- IBA Acquires Radcal to Expand Medical Imaging Quality Assurance Offering
- International Societies Suggest Key Considerations for AI Radiology Tools
- Samsung's X-Ray Devices to Be Powered by Lunit AI Solutions for Advanced Chest Screening
- Canon Medical and Olympus Collaborate on Endoscopic Ultrasound Systems








.jpg)










.jpg)
.jpg)